n8n vs OpenAI AgentKit: What We Learned in Our Deep Dive
OpenAI officially enters the agent-building arena with AgentKit. We compare its architecture, developer experience, and UI capabilities against n8n and Inkeep to help developers choose the right framework.
SUMMARY
AgentKit delivers polished chat experiences with rich widget rendering, but forces developers into rigid sequential workflows with manual if/else routing for multi-agent collaboration
n8n offers more agent autonomy and model flexibility with hundreds of integrations, but lacks the sophisticated chat UI needed for modern applications
While AgentKit excels at UI polish and n8n dominates backend automation, both require workarounds for complex multi-agent scenarios
Inkeep eliminates the trade-offs by combining AgentKit's UI sophistication with n8n's autonomous routing, plus true no-code agent delegation
Today, October 6, 2025, OpenAI has officially entered the agent-building arena with the launch of AgentKit. As a major force in the AI ecosystem, OpenAI's entry with a new visual workflow builder is a significant event. But for developers already working with powerful existing tools, the critical question is: how does this brand-new platform stack up against the competition?
To answer this question, I spent a full day playing around with AgentKit & n8n to see how they compare in terms of their architecture, developer experience, and UI capabilities.
We'll examine AgentKit's strengths and weaknesses relative to the open-source automation powerhouse n8n, and introduce Inkeep, a comprehensive agent platform that aims to provide the best of both worlds, and more.
OpenAI's AgentKit: The Polished Chat Experience
As a brand-new offering, AgentKit's primary strength lies in its tight integration with ChatKit, an open-source library for creating sleek, modern chat interfaces.
Where AgentKit Shines
- Seamless Chat Integration: ChatKit provides a polished, out-of-the-box solution for deploying agents. This focus on the front-end experience makes AgentKit an attractive option for projects where the user-facing chat interface is the top priority.
- Rich UI Rendering: AgentKit excels at creating visually appealing chat experiences. Its Widget Builder allows developers to generate custom UI components using natural language, which can then be easily dropped into a workflow. The platform automatically structures the agent's output to match the widget, streamlining the process of building interactive, user-friendly applications.
- Beginner friendly interface: AgentKit's interface is designed to be easy to use for beginners. It provides a visual workflow builder with a drag-and-drop interface, and a set of pre-built templates for common use cases.
- Comprehensive developer SDK: AgentKit provides a comprehensive Agent SDK (TypeScript/Python) for programmatic agent definition. Moreover, you can turn your AgentKit workflows into Agent SDK code.
Architectural and Developer Experience Challenges
Despite its UI prowess, AgentKit's underlying architecture presents several hurdles that can increase development overhead.
1. Rigid, Sequential Routing for subagents and chat widgets
- Agents in AgentKit can only connect directly with one other subagent at a time. To connect with multiple subagents, you must use a complex
if/elsenode to manage decision-making, which erodes the agentic experience. Moreover AgentKit agents cannot intelligently select whether they output text or a chat widget, it is either one or the other. Instead, developers must manually insert anif/elsenode to manage decision-making. This adds an extra, often cumbersome, step. In contrast, frameworks like Inkeep allow an agent to autonomously choose the correct subagent or widget based on the needs of the situation.
Example: A simple customer support agent
- In AgentKit, a simple customer support agent with rich UI rendering requires 4 separate agents: an agent to determine whether the knowledge base answers the customers question, a second agent to provide a response if the knowledge base does answer the question, a third agent to notify the customer that they are creating a zendesk ticket, and a fourth agent to create the ticket and produce the chat widget.
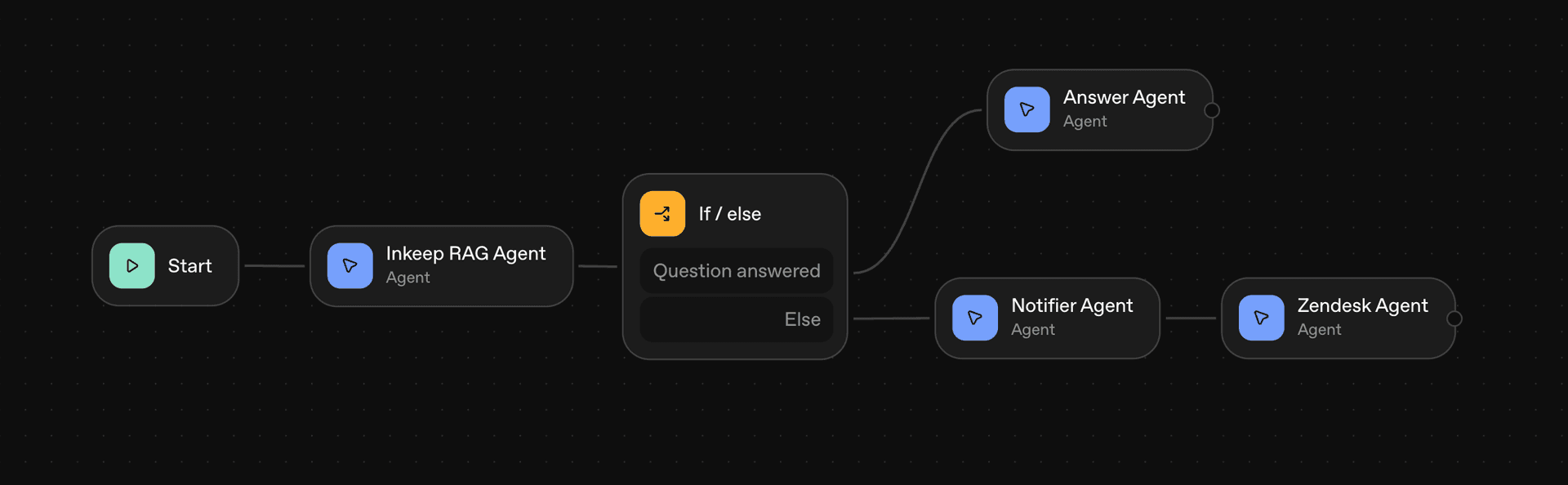
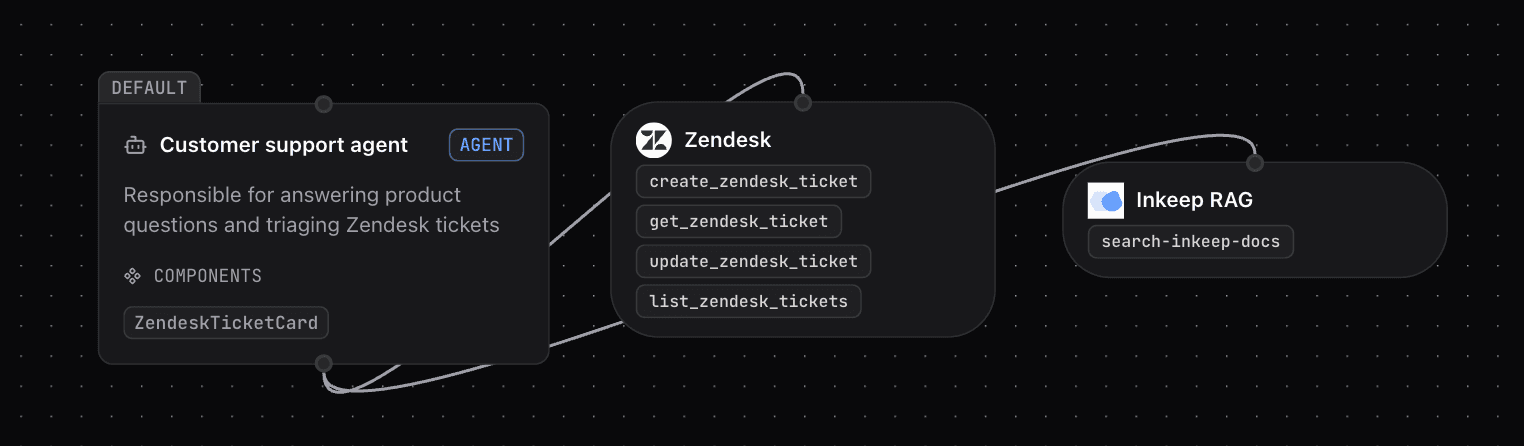
- In Inkeep, for example, this is accomplished with just one agent. Because agents are not solely locked in to creating a text output or chat widget output, the same agent can both answer customer questions and produce a chat widget for Zendesk tickets created.
2. Deployment options are limited
- Because AgentKit is a closed-source platform, users do not have the option to self-host and you must use their cloud-hosted solution. This contrasts with n8n and Inkeep, both of which are open-source and self-hostable.
3. Limited ways to consume your agents
- AgentKit agents can only be consumed via their ChatKit library. n8n and Inkeep agents on the other hand can be consumed via their own UI libraries, http requests, and even as MCP servers. Inkeep in particular allows you to consume your agents through the Vercel AI SDK and A2A protocol.
4. Ecosystem & Vendor Lock-In
- AgentKit exclusively supports OpenAI models. This limits flexibility and prevents developers from leveraging models from providers like Anthropic, Google, etc. Inkeep and n8n on the other hand support a wide range of models including through OpenRouter.
5. No Code to UI Interoperability
- While AgentKit allows you to export a visual workflow to the Agent SDK, this is a one-way street. You cannot import your Agent SDK code to create a visual workflow.
n8n: The Open-Source Automation Powerhouse
n8n stands in stark contrast to AgentKit, prioritizing flexibility, customizability, and developer freedom. It does much better in terms of creating autonomous, agentic workflows.
Key Advantages of n8n:
- Open-Source and Model-Agnostic: As an open-source platform, n8n offers complete transparency and customizability. It integrates with hundreds of models, giving developers the freedom to choose the best LLM for their specific needs.
- Powerful Automation: At its core, n8n is a robust workflow automation tool with a vast library of integrations, making it ideal for complex back-end processes.
- More ways to trigger your agents: n8n agents can be triggered via http requests, webhooks, cron jobs, MCP servers, form submissions, and more.
Limitations:
While powerful on the back-end, n8n's front-end chat UI is less developed than AgentKit's and Inkeep's with limited customization options. Moreover, n8n lacks the rich, generative UI that comes with AgentKit and Inkeep.
Additionally, while the autonomy of its agents are a big step up from AgentKit's, agents in n8n still cannot autonomously send messages to their subagents. Rather, n8n subagents must predefine what structured input from the parent agent they expect using n8n's fromAI() syntax in its prompt.
This step means that to create truly autonomous agents with n8n, you have to introduce some code which adds additional overhead to the builder experience.
Finally, n8n doesn't support bidirectional conversion between workflows and code. While you can export workflows as JSON and import them back, this isn't true code generation or code-to-workflow conversion.
Inkeep: The Best of Both Worlds and Beyond
Inkeep is an alternative that combines the UI polish of AgentKit with model and trigger flexibility of n8n. Inkeep is great for both conversational assistants with out-of-box UI components in addition to agentic workflows, both powered by a multi-agent architecture that is less rigid than either n8n or AgentKit.
Where Inkeep comes in
1. True Multi-Agent and Agent-driven Architecture
- In contrast to AgentKit, Inkeep agents can connect to multiple subagents directly and autonomously determine which agent to use. No
if/elsecode blocks or complex expressions like$input.output_parsed.classification == "flight_info"are required. Moreover, in contrast to n8n, Inkeep agents automatically send relevant messages to their subagents, rather than having to define from your subagents which information you would like to be called with. Lastly, Inkeep agents can autonomously determine whether they output text or a chat widget, reducing workflow complexity.
2. Better Developer Experience:
- Simplified Tool Management: Define your MCP servers once and then freely connect them across your workflows. Moreover, the UI provides at-a-glance clarity on which models each agent is using and which tools each MCP server carries.
- Dynamic Context Injection: Inkeep allows you to make API calls or fetch data and inject it directly as context into your workflow's first agent. In AgentKit, this would require wrapping the API call in a custom tool server, adding an unnecessary configuration and runtime step.
- Lightweight Frontend Integration: Instead of setting up a dedicated back-end endpoint to manage client secrets, you simply pass the agent URL and an API key into Inkeep's open-source UI component library.
3. Customizable and Powerful Chat UI:
- Inkeep's open-source component library is more customizable than n8n's and enables the kind of rich UI rendering that AgentKit also introduces. It gives developers the ability to define custom UI components that map to structured LLM outputs to create interactive UIs with messages that go beyond plain text.
Feature Comparison at a Glance
| Feature | AgentKit (OpenAI) | n8n | Inkeep |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Agent Routing | Manual (if/else nodes required) | Autonomous (Intelligent tool selection) | Autonomous (Natural language-based routing) |
| Developer Experience | Streamlined, intuitive, with some code | Flexible but can be complex | Streamlined, intuitive, and truly no-code |
| Chat UI | Excellent, rich widgets via ChatKit | Basic and less customizable | Excellent, highly customizable rich UI components |
| Model Support | OpenAI models only | Open (supports hundreds of models) | Open (supports all major models) |
| Source Code | Closed Source | Open Source | Open Source |
| Frontend Integration | Complex (requires back-end for client secrets) | Simple (pass in webhook URL) | Simple (API key and URL passed to component) |
| Code Export | One-way workflows to code | JSON format | Two-way workflows to code and vice versa |
| Deployment | Cloud-hosted | Self-hosted and cloud-hosted | Self-hosted and cloud-hosted |
| Ways to consume your agents | ChatKit library | HTTP requests, webhooks, cron jobs, MCP servers, form submissions, and more. | HTTP requests, webhooks, cron jobs, MCP servers, form submissions, Vercel AI SDK, A2A protocol, and more. |
| Tracing | Logs are in a separate dashboard | Live trace logging | Live trace logging |
| Evaluation | Evaluation through natural language prompts | Evaluation nodes which read from spreadsheet | Third-party evaluation tools like Langfuse |
Conclusion
Choose AgentKit if you prioritize a polished chat interface with rich widget rendering and are building simple, linear workflows. It's ideal for beginners who want an intuitive visual builder and don't mind being locked into OpenAI's ecosystem. However, be prepared for increased development overhead due to rigid sequential routing that requires manual if/else nodes for any complex agent interactions.
Choose n8n if you need a powerful, open-source automation platform with maximum model flexibility and extensive integration capabilities. It's perfect for complex back-end workflows where you can tolerate a less developed chat UI and are comfortable with some coding requirements for truly autonomous agent behavior. The platform excels when rich conversational interfaces aren't your primary concern.
Choose Inkeep if you want the best of both worlds without compromise. It combines AgentKit's polished UI capabilities with n8n's autonomous routing flexibility, while adding truly no-code agent delegation through natural language. With superior developer experience, lightweight frontend integration, and a highly customizable open-source component library, Inkeep is ideal for building sophisticated, production-ready AI Agents that can scale from simple chat interfaces to complex multi-agent workflows.
If you are interested in a video comparison of AgentKit and n8n, you can watch the following video:
Frequently Asked Questions
AgentKit is OpenAI's new visual workflow builder for creating AI Agents. It launched on October 6, 2025, featuring tight integration with ChatKit for creating modern chat interfaces. However, it uses rigid sequential routing that requires manual if/else nodes for multi-agent collaboration and rich UI rendering.
AgentKit has several key limitations: rigid sequential routing requiring manual if/else nodes for multi-agent workflows, exclusive OpenAI model support, and no code-to-UI import capability.
While AgentKit excels at creating polished chat interfaces with rich UI widgets through ChatKit integration, it suffers from rigid sequential routing that requires manual if/else nodes for multi-agent workflows. n8n offers more autonomous agentic behavior where agents can intelligently route tasks based on descriptions, plus it's open-source and model-agnostic with hundreds of integrations. However, n8n's chat UI is less developed than AgentKit's widget-based interface, and it still requires some coding for truly autonomous subagent communication through its fromAI() syntax.
Inkeep combines AgentKit's polished UI capabilities with n8n's autonomous routing, while adding truly no-code agent delegation using natural language. It offers simplified tool management, dynamic context injection, lightweight frontend integration, and a highly customizable open-source component library.
No, AgentKit is a closed-source platform that exclusively supports OpenAI models. This creates vendor lock-in and prevents developers from leveraging models from providers like Anthropic, Google, or others. Both n8n and Inkeep support multiple model providers.